-
What Is Implied Consent?
If you’ve been charged with drunk driving, you will need to have an attorney in Owings Mills explain the legal nuances of your case. Like other states, Maryland has established a rule of implied consent. This means that, if you are driving on the state’s roadways, you are presumed to have already consented to submit to a blood, breath, or urine test. The implied consent law applies to you if you’re pulled over by a police officer on suspicion of impaired driving and the officer asks you to submit to blood alcohol content (BAC) testing.
Since every driver has already given his or her consent to submit to testing, drivers who refuse to do so face legal penalties. If you’ve refused to take the test, your lawyer will inform you that you face a 120-day suspension of your driver’s license. If you refuse the test on a second occasion, the suspension will last for one year. Some people reason that it’s worth it to risk license suspension if it means they won’t be convicted of DUI. But in fact, refusal to submit to a test almost certainly won’t help your case, and it will only add to the penalties you could face.

-
Common Questions About Supervised Visitation in Maryland
During a divorce in which the spouses share children in common, a family law attorney in Owings Mills can help the parties develop a proposed visitation plan. Normally, visitation occurs at the parent’s house. Occasionally, a judge may order supervised visitation, in which a neutral third party is present for the entire visitation to ensure the safety of the children. If you have concerns about your children’s safety when they are with your ex, talk to your custody lawyer about requesting supervised visitation.

Can I request supervised visitation for my ex?
Maryland family courts generally only require a parent to have supervised visitation if there is a reasonable belief that a child has been neglected or abused by that parent. It is not sufficient to request supervised visitation because you’re concerned the other parent might not help the kids with their homework or enforce limits on TV time. But if you do have reason to believe that your kids are not safe with the other parent, don’t hesitate to voice your concerns to the divorce lawyer.
Where does supervised visitation take place?
This is determined on case-by-case basis. Occasionally, the judge may allow supervised visitation to take place in the home of another relative. Alternatively, supervised visitation may occur at a family services center under the direction of a court-appointed facilitator.
Is supervised visitation the same as a monitored exchange?
Family service centers may also provide monitored exchange programs, but these are not the same as supervised visitation. A monitored exchange program allows the parent to drop off the child at the center and then leave. The other parent then picks up the child for unsupervised visitation.
Is there a fee for supervised visitation?
Some family service centers do charge fees, while others offer free services. Some centers require both parents to pay an upfront intake fee and the visiting parent to pay the hourly charges.
How will I know that my child is safe?
When your child is at a supervised visitation, you can rest assured that he or she will be closely watched by the staff. Staff members are trained to intervene whenever it is necessary to promote appropriate interactions between the parent and child. These staff members have experience working with children affected by divorce and separation, and they can help your child feel safe and secure.
-
A Quick Look at the New DUI Law in Maryland
If you’ve recently consulted a lawyer in Owings Mills about legal representation for your DUI case, you may be informed of a new law that recently took effect this fall. DUI lawyers in Maryland have been evaluating the possible effects of Noah’s Law on their clients. The law was named in honor of a 24-year-old police officer in Montgomery County, Noah Leotta, who was killed during a routine traffic stop when a drunk driver struck him.
The new law mandates that any driver who is convicted of DUI or DWI is required to have an ignition interlock device installed. While ignition interlock devices are nothing new, what makes this law especially aggressive is that drivers can be required to use the devices for six months if a chemical test reveals a blood alcohol content (BAC) of 0.08% or higher-regardless of whether or not the drivers are convicted. If a driver refuses a Breathalyzer test, the interlock device must be used for nine months or the driver’s license will be suspended.

-
An Inside Look at the Divorce Process
If you are eligible for divorce in Maryland , there are several steps you and your spouse must take to legally end your marriage. In addition to making the decision to divorce, you must also settle matters such as asset division, child custody, and spousal support. Working with a divorce attorney serving Owings Mills is a smart choice when navigating Maryland divorce laws; your divorce lawyer will ensure that all relevant issues are covered and that your needs and preferences are met during the divorce process.
Filing Divorce Documents
 The first step in seeking a divorce in Maryland is the filing of at least two documents: A Complaint for Absolute Divorce and a Civil Domestic Case Information Report. These documents must be filed by the plaintiff spouse wishing to end the marriage with the circuit court serving your county, and are associated with filing fees; however, you may be eligible for a fee waiver depending on your circumstances.
The first step in seeking a divorce in Maryland is the filing of at least two documents: A Complaint for Absolute Divorce and a Civil Domestic Case Information Report. These documents must be filed by the plaintiff spouse wishing to end the marriage with the circuit court serving your county, and are associated with filing fees; however, you may be eligible for a fee waiver depending on your circumstances.Serving of Divorce Documents
After the divorce documents have been filed, the defendant spouse is personally served with these documents, as well as a Writ of Summons. The plaintiff spouse will receive an affidavit proving that the papers have been served once this process is complete.
Filing an Answer
Once the defendant spouse receives the divorce documents, he must file an Answer to the Complaint for Absolute Divorce. This document will admit or deny any allegations made in the Complaint. Additionally, the defendant spouse has the right to file a Counter Complaint for Absolute Divorce, which may state grounds for divorce that are different than those of the plaintiff spouse if he disagrees with the original Complaint.
Settlement Process
Before the divorce can be finalized, both spouses must settle issues such as the division of finances and property, child custody and support, and alimony payments. This process is typically aided by the couple’s family court attorneys, and may go through a divorce mediation process or court appearances if the couple cannot come to an agreement on the terms of the divorce.
-
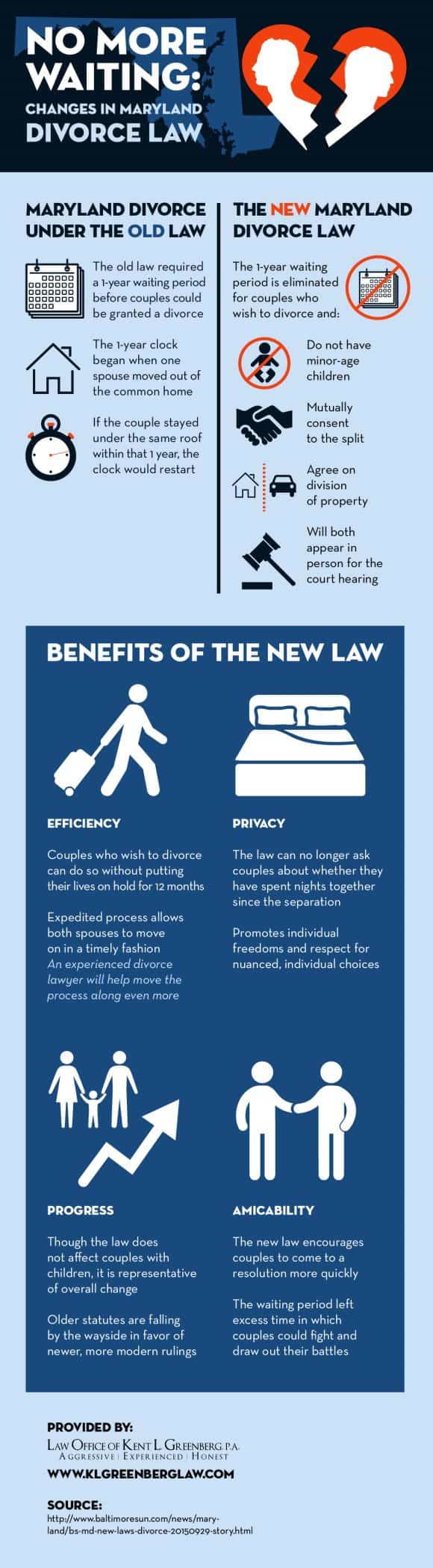
No More Waiting: Changes in Maryland Divorce Law
While most couples who marry hope to stay together for the rest of their lives, divorce is a possibility. If you and your spouse agree that you cannot stay married, a divorce can be the best choice for both of you. Up until recently, couples in Maryland who wanted to get a divorce had to wait one year from the time one spouse moved out to make the separation official. Thanks to a new law, however, couples without minor children who can agree on the division of property no longer have to wait. This expedited divorce process indicates progress in the area of divorce law, and respects the privacy of both parties more than the old law. Take a look at this infographic from a divorce lawyer in Owings Mills to learn more about what the new law means for couples in Maryland who are divorcing.
-
Comparing Limited and Absolute Divorce in Maryland
Compared to many other states, such as California, Maryland has relatively strict laws regarding divorce. Spouses may file for limited divorce or absolute divorce, but only based on certain grounds. When you meet with divorce lawyers in Owings Mills, you can learn more about filing for limited or absolute divorce.
Differences Between Limited and Absolute Divorce
Maryland family law defines limited divorce as a legal separation. If the court grants a limited divorce , you are not actually divorced. Legally, you are still married to your spouse and you may not remarry. Spouses may seek a limited divorce when there are certain issues that they need to resolve through the court. In contrast, an absolute divorce is a permanent dissolution of the marriage. A divorce decree settles issues such as property division. Once a divorce decree is issued by the court, the divorce is finalized and either party is free to remarry.
 Grounds for Limited and Absolute Divorce
Grounds for Limited and Absolute Divorce Maryland divorce laws establish four grounds for seeking a limited divorce. They are the unjustified abandonment of a spouse, cruelty of treatment, and/or vicious conduct toward a spouse or minor child. The fourth basis is established if the spouses have been living separately. It is not strictly necessary to obtain a limited divorce before filing for an absolute divorce. Spouses can file for absolute divorce if they have been living apart from each other continuously for one year, without having had sexual relations during that time. A spouse can file for absolute divorce before this one-year mark if he or she can prove adultery, desertion, cruel treatment, insanity, or incarceration of the other spouse. Sometimes, couples can file for an absolute divorce based on mutual consent. This applies if they do not have any minor children in common and they submit to the court a written, signed settlement agreement that resolves all issues.
Issues Resolved Through Divorce
A limited or an absolute divorce can resolve a number of issues. Limited divorce can address matters pertaining to child custody, child support, spousal support, and the use and possession of property. Similarly, an absolute divorce resolves issues such as child custody, child and spousal support, property division, and surname changes.
RECENT POSTS
categories
- Uncategorized
- Divorce
- Infographic
- reviews
- Accidents
- Divorce Law
- Maryland Divorce Law
- Child Custody
- Alimony
- Indefinite Alimony
- Divorce Lawyer
- Annulment
- Kent L. Greenberg
- Matthew J. Rudo
- Child Support
- Credit Card Debt
- Remarriage
- Divorce Papers
- Child support law
- Alimony laws
- divorce process
- Alimony Payments
- Absolute Divorce
- Contested Divorce
- divorce attorney
- family attorney
- family law
- No-Fault Divorce
- Family Care Plan
- financial statement
- Online Divorce
- lawyer
- Uncontested Divorce
- Law Office of Kent L. Greenberg
- P.A.
- Joint Custody
- Senior Divorce
- DIY Divorce
- Car Accident Attorney
- Greenberg
- Personal Injury Law
- Domestic violence
